用所给动词的正确形式填空。l. Her family invited me_____ (stay) with them for a few weeks.2. I need _____(do) some shopping on my way home from work.3. I've-九年级英语
hung, hung(挂,吊)
d. welcome(欢迎)一词是规则动词,不可误用为不规则动词
welcome welcomed, welcomed(正)
welcome, welcome(误)
e.不要将不规则动词误用为规则动词
hit(打)
hit, hit(正)
hitted, hitted(误)
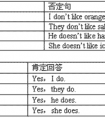
1.主+V-ed+宾+其它。。。(肯定句)
2.主+didn't+V原+宾+其它。。。
3.Did+主+V原+宾+其它。。。+?
4.回答:Yes,主语代词+did\No,主语代词+didin't.
5.特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句。
肯定句要使用动词的过去式,否定句和疑问句要使用助动词do和 does 的过去式 did.
肯定句为:
主语+动词过去式+宾语 如:
I went home at nine o'clock yesterday.
否定句:
主语+didn't +动词原形+宾语 如:
I didn't go home yesterday. He didn't tell me about you.
疑问句:
一般疑问句:
Did +主语+动词原形+宾语
如:Did you go home yesterday?
Did you study in the school?
肯定回答: Yes, I did.
否定回答:No, I didn't.
特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+did +主语+动词原型+宾语
When did you finish your homework last night?
What did you do the day before yesterday?
考点名称:实义动词
- 实意动词:
即行为动词,表示动作的动词。实义动词与系动词是相对的,能独立用作谓语。
它分为及物动词和不及物动词两种:
及物动词是指后面要求有直接宾语的动词;
不及物动词指后面不需要跟宾语的动词。 实意动词使用方法:
及物动词
后面必须跟宾语意义才完整的实义动词,叫做及物动词(transitive verb)。如:
I believe that the committee will consider our suggestion.我相信委员会将会考虑我们的建议。
“How long can I keep the book ?”Harry asked.哈里问:“这本书我可以借多久?”
Dr. Bethune set us a good example. 白求恩大夫给我们树立了好榜样。
Crude oil contains many useful substances.原油含有许多有用的物质。
不及物动词
本身意义完整后面不须跟宾语的实义动词,叫做不及物动词(intransitive verb)。如:
Birds fly.鸟会飞。
It happened in June 1932.这件事发生于一九三二年六月。
My watch stopped.我的表停了。
She spoke at the meeting yesterday evening. 她在昨天晚上的会上发了言。
兼作及物动词和不及物动词
英语里有不少实义动词可以兼作及物动词和不及物动词。这样的动词又有两种不同的情况
a)兼作及物动词和不及物动词时,意义不变。试比较:
Shall I begin at once?我可以立刻开始吗?(begin作不及物动词)
She began working as a librarian after she left school.她毕业后当图书馆管理员。(began作及物动词)
When did they leave Chicago?他们是什么时候离开芝加哥的?(leave 作及物动词)
They left last week. 他们是上周离开的。(left 作不及物动词)
b)兼作及物动词和不及物动词时,有时意义不尽相同。如:
Wash your hands before meals.饭前要洗手。
Does this cloth wash well? 这布经得起洗吗?- 英汉实意动词用法比较:
与汉语的比较,有时英语动词的及物和不及物的用法,与汉语的用法不一样,请注意下列两种情况:
a)有的动词在英语里只能用作不及物动词,而汉语则可用作及物动词,如arrive到达,agree同意,listen听。英语里这些动词后面常接介词。如:
We arrived at the railway station at noon.
我们于中午到达火车站。(at不能省去)
(比较:We reached the railway station at noon.)
Everybody listened to the lecture with great interest.
每个人都很有兴趣地听讲课。(to不可省去)
(比较:We all heard the lecture.)
Do they agree to the plan?他们同意这个计划吗?(to不可省去)
b)有的动词在英语里能用作及物动词,而在汉语里则不能用作及物动词,如serve为…服务。
Our children are taught to serve the people wholeheartedly.
我们的儿童被教以全心全意为人民服务
用于be动词之后,实义动词之前。 实意动词的用法:
肯定句:
主语+动词过去式+其它
否定句:
主语+助动词didn‘t+动词原型+其他
一般过去式:
Did+主语+动词原型+其他
考点名称:一般将来时
一般将来时:
表示将来某一时刻的发生动作或状态,或将来某一段时间内经常的动作或状态。
一般句型有:
肯定句:
I/We shall/will go. You/He/She/They will go.
否定句:
I/We shall/will not go. You/He/She/They will not go.
疑问句:
Shall I/we go? Will you/he/she/they go?
简略回答:
(肯)Yes,主语shall/will (否) No,主语 shall/will not
特殊疑问句:
一般将来时的特殊疑问句是将疑问词放在句首,后接一般疑问句(就主语提问时,以疑问词who开头的疑问词除外)
Why will you be here on Sunday?(周日你为什么将要在这儿?)
I will have a meeting on Sunday(我将要在周日举行一个聚会)
(对特殊疑问句要进行具体回答)
一般疑问句:
be或will提到句首,some改any,and改or,第一二人称互换
We are going to go on an outing this weekend.
Are you going to go on an outing this weekend?
被动句:
will/shall+be+v.ed(及物动词过去分词)
The letter will be sent tomorrow.
这封信明天将寄出去
We shall be punished if we break the rule.
如果我们违反规定,我们将受到惩罚。- 一般将来时的构成:
1. 用will或shall表示
“助动词will或shall+动词原形”这一形式,表示将来发生的事情,用于征求对方的意见或表示客气的邀请。在口语中will用于所有人称,书面语中第一人称常用shall,如:
①Tomorrow will be Sunday. 明天就是星期天。
②The rain will stop soon. 雨很快就要停了。
③Shall we go there at five? 我们五点钟去那儿,好吗?
④Will you please open the door? 请你把门打开,好吗?
2. 用be going to结构表示
“be going to+动词原形”用来表示近期或事先考虑过的将要发生的动作以及已有迹象 表明必将发生某事,意为“打算;就要”。如:
①We’re going to meet outside the school gate. 我们打算在校门口见面。
②Look! It's going to rain. 瞧!快下雨了。
3. 用现在进行时表示
表示位置转移的动词(如:go, come, leave, start, arrive等),可用现在进行时表示将来时。如:
①Uncle Wang is coming. 王叔叔就要来了。
②They’re leaving for Beijing. 他们即将前往北京。
4. 用一般现在时表示
根据规定或时间表预计要发生的动作,在时间和条件状语从句中,都可用一般现在时表示将来时。如:
①The new term starts (begins) on August 29th. 新学期八月二十九日开学。
②If it doesn’t rain tomorrow, we will go out for a picnic.
如果明天不下雨,我们将出去野餐。
5. 用“be+动词不定式”或用“be about to +动词原形”的结构表示,如:
①He is to visit Japan next year. 明年他将访问日本。
②They’re about to leave. (=They’re leaving.) 他们就要走了。 be going to与will的区别:
be going to与will两者都可表示将要发生的事、将要去做某事,但它们有如下几点区别:
1. be going to 表示近期、将要发生的事情,will 表示的将来的时间则较远一些,如:
He is going to write a letter tonight.
He will write a book one day.
2. be going to 表示根据主观判断将来肯定发生的事情,will表示客观上将来势必发生的事情。
He is seriously ill. He is going to die.
He will be twenty years old.
3. be going to 含有“计划,准备”的意思,而 will 则没有这个意思,如:
She is going to lend us her book.
He will be here in half an hour.
4.在有条件从句的主句中,一般不用 be going to, 而多用will, 如:
If any beasts comes at you, I'll stay with you and help youshall和will区别:
1.shall和will常常缩写成'll,紧接在主语之后。其否定式 shall not 和will not 的缩写式分别为 shan't 和 won't。
- 最新内容
- 相关内容
- 网友推荐
- 图文推荐
| [家长教育] 孩子为什么会和父母感情疏离? (2019-07-14) |
| [教师分享] 给远方姐姐的一封信 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 伸缩门 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 回家乡 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 是风味也是人间 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 一句格言的启示 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 无规矩不成方圆 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 第十届全国教育名家论坛有感(二) (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 贪玩的小狗 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 未命名文章 (2018-11-07) |


![Sunday is my birthday. I would like _____ a birthday party, would you _____to my party? [ ]A. have; come B. to have; to come C. have; to come D. to have-七年级英语](http://www.00-edu.com/d/file/ks/4/2/budingshi/2020-01-08/smalla85122db0c71d7fb6ae58187be7f1fd11578430330.png)
![Why areyou here? You are supposed ______ in the classroom now. [ ] A. to studyB. to be studiedC. studying D. to be studying -九年级英语](http://www.00-edu.com/d/file/ks/4/2/budingshi/2020-01-08/small6dee02daa62cac1c71853ac804ab4fbd1578422460.png)
![She is very poor. Little food _____ and no room _____! [ ]A. to eat, to live B. to eat, to live in C. eating, living -八年级英语](http://www.00-edu.com/d/file/ks/4/2/budingshi/2020-01-09/small17b77c2697a3ef8f1461d0d14b016ee51578585185.png)
