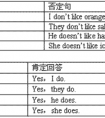
改错。( ) 1.Whatareyourfatherlike?A B C() 2.Doestheyhaveanewteacher?A B C() 3.—Ishestrict? —No, sheisn't.AB C() 4.Hismusicteacherisyoungorpretty.A B C(-五年级英语
will be
一般时态有关be动词的口诀:
我用am,你用are,is连接他/她/它,复数形式就用are
be动词的用法:
现在时 I am, you are, he is, we are, you are, they are
(缩略式 I'm, you're, he's, we're, you're, they're),
(否定缩略式 I'm not, isn't, aren't),
过去时 I was, you were, he was, we were, you were, they were
(过去时否定缩略式 wasn't, weren't),
过去分词been,现在分词being
英语的“be”是个特殊动词;有些语言,如马来文等,并没有“be”这样的动词。
“Be”除了原形的“be”之外,还有另外七种形式:
am, is, are, been, being, was, were.
在句子中,“be”可以是主动词(The Principal Verb)或助动词(The Auxiliary Verb)
一、口诀:
我用am,你用are,is连着他,她,它;
单数名词用is,复数名词全用are;
变疑问,往前提,句末问号某丢弃;
变否定,更容易,be后莫忘记;
疑问否定任你变,句首大写莫迟疑。
二、Be动词在一般过去时中的变化:
1、am和is在一般过去时中变为was;
2、are在一般过去时中变为were
3、带有was或were的句子,其否定、疑问的变化和am is are一样,即否定句在was或were后加 not,一般疑问句把was或were调到句首。
考点名称:人称代词
人称代词:
代词是为了避免重复,用来代替前面提到过的人、动物、事物名称的词。人称代词主要用来指人,也能用来指物。人称代词分主格和宾格。人称
单数
复数
主格
宾格
主格
宾格
第一人称
I
me
we
us
第二人称
you
you
you
you
第三人称
he
him
they
them
she
her
it
it
- 人称代词主宾口诀:
人称代词分主/宾,只有八对要区分。
你(们)、它主/宾同一形,其余主/宾须分清。
谓语之前主格填,动/介之后宾格跟,
口语运用最灵活,表语也可用宾格。
人称代词并列现,注意顺序礼貌见,
二一、三一、二三一,第一人称最谦虚,
若把错误责任担,第一人称须当先。
考点名称:助动词
助动词:
协助主要动词构成谓语动词词组的词叫助动词,被协助的动词称作主要动词。
构成时态和语态:助动词是语法功能词,自身没有词义,不可单独使用,它没有对应的汉译,
例如:Hedoesn'tlikeEnglish.他不喜欢英语。(doesn't是助动词,无词义;like是主要动词,有词义)- 小学涉及到的助动词主要是do,以及它的两种时态:does和did。
例:Does he work in the factory? 他是在这个工厂工作吗?
Do you have a pen? 你有一支钢笔吗?
He didn’t go to school yesterday. 他昨天没有去上学。
助动词do 的用法:
1)构成一般疑问句,例如:
Do you want to pass the CET? 你想通过大学英语测试吗?
Did you study German? 你们学过德语吗?
2) do + not 构成否定句,例如:
I do not want to be criticized. 我不想挨批评。
He doesn't like to study. 他不想学习。
In the past, many students did not know the importance of English. 过去,好多学生不知道英语的重要性。
3)构成否定祈使句,例如:
Don't go there. 不要去那里。
Don't be so absent-minded. 不要这么心不在焉。
说明: 构成否定祈使句只用do,不用did和does。
4)放在动词原形前,加强该动词的语气,例如:
Do come to my birthday party. 一定来参加我的生日宴会。
I did go there. 我确实去那儿了。
I do miss you. 我确实想你。
5) 用于倒装句,例如:
Never did I hear of such a thing. 我从未听说过这样的事情。
Only when we begin our college life do we realize the importance of English.
只有在开始大学生活时我们才认识到英语的重要性。
说明: 引导此类倒装句的副词有never, seldom, rarely, little, only, so, well等。
6)用作代动词,例如:
---- Do you like Beijing? --你喜欢北京吗?
---- Yes, I do. --是的,喜欢。(do用作代动词,代替like Beijing.)
He knows how to drive a car, doesn't he?
他知道如何开车,对吧? - 基本助动词:
be, do, have, 他们没有词汇意义,只有语法作用,如协助构成进行体,完成体,被动态,否定句,疑问句等。
例如 He is giving a lecture. 他在作报告
He has made a plan. 他已经订了计划
The small animals are kept in the cages. 小动物都关在笼子里。
助动词协助主要动词完成以下功用:
a. 表示时态,例如:
He is singing. 他在唱歌。
He has got married. 他已结婚。
b. 表示语态,例如:
He was sent to England. 他被派往英国。
c. 构成疑问句,例如:
Do you like college life? 你喜欢大学生活吗?
Did you study English before you came here? 你来这儿之前学过英语吗?
d. 与否定副词not合用,构成否定句,例如:
I don't like him. 我不喜欢他。
e. 加强语气,例如:
Do come to the party tomorrow evening. 明天晚上一定来参加晚会。
He did know that. 他的确知道那件事。
考点名称:连词
- 连词:
是连接单词、短语或句子的一种词,连词不能独立担任句子成份,而只起连接作用。
连词可分为两大类:并列连词和从属连词。 - 连词的用法:
一、并列连词:
1.and连接单词MybrotherandIstudyinthesameschool。
连接短语Ourknowledgemaycomefromthebooksandfrompractice。
连接句子Wearesingingandtheyaredancing。
2but但是/而是Ihaveapenbutnopencil.or或者Willyougotherebybusoronfoot
3.nothingbut除了,只有Ididnothingbutwatchit。
4.or表示否则Hurryuporyouwillbelate。
5.for表示因为Heisgoodatmathforhestudiesharderthanothers。
二、从属连词:
1.after表示“时间”,在…之后
AfterIfinishedtheschool,Ibecameaworkerinthefactory。
2.although/though表示让步,“尽管”Althoughsheisyoung,sheknowsalot。
3.as表示时间,“当…时”,方式“象…”,原因,“由于、因为”让步,“尽管、虽然”
Asitwaslate,wemustgonow。
4.asif/asthough表方式,“似乎、好像”
Hetoldissuchastoryasthoughhehadbeentherebefore。
5.aslongas/solongas表条件,“只要”AslongasIamfree,I’llgotohelpyou。
6.assoonas表时间,“一…就…”IwillphoneyouassoonasIcomeback。
- 最新内容
- 相关内容
- 网友推荐
- 图文推荐
| [家长教育] 孩子为什么会和父母感情疏离? (2019-07-14) |
| [教师分享] 给远方姐姐的一封信 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 伸缩门 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 回家乡 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 是风味也是人间 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 一句格言的启示 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 无规矩不成方圆 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 第十届全国教育名家论坛有感(二) (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 贪玩的小狗 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 未命名文章 (2018-11-07) |