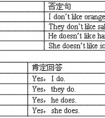
改错。( ) 1. JuststayonbedandI'lltelephonethedoctor. _________________ A B C( ) 2. You'dbettertogotothehospital. _________________ A BC( ) 3.Howmanyfishes-六年级英语
其用法特点为:
是不可数名词,只用单数形式,不用不定冠词(当然更不能用数词),没有复数形式。
如:Our clothing protects us from [against] the cold. 我们的衣服可以御寒。
Have you checked all your baggage? 你所有的行李都托运了吗?
The thief stole all her jewelry. 小偷把她所有的首饰都偷走了。
The hospital has no decent equipment. 这家医院没有像样的设备。
The Tang Dynasty is thought of as the high summer of Chinese poetry. 人们认为唐朝是中国诗歌的全盛时期。
注:machinery, poetry, jewelry, scenery等相应的个体可数名词是 machine, poem, jewel, scene等。
如:a poem / a piece of poetry 一首诗
many machines / much machinery / many pieces of machinery 许多机器
第五类
补充几个常考的集合名词除上面提到的四类集合名词外,以下几个集合名词也应重点注意:
1. hair(头发,毛发)
指全部头发或毛发时,为集合名词(不可数);指几根头发或毛发时,为个体名词(可数)。
如:My hair has grown very long. 我的头发已长得很长了。
The police found two hairs there. 警察在那儿找到了两根头发。
2. mankind(人类)
人是一个不可数的集合名词,不用复数形式,也不连用冠词。
如:This is an invention that benefits mankind. 这是一项造福人类的发明。
Mankind has its own problems. 人类有自己的问题。
注:mankind 表示“mankind 人(类)”时,虽不可数,但有时却可以表示复数意义,尤其是当其表语是复数时。
如:Mankind are intelligent animals. 人是理智的动物。
3. fruit(水果)
作为集合名词,它通常是不可数的。
如:He doesn’t eat much fruit. 他不大吃水果。
He is growing fruit in the country. 他在乡下种水果。
但是,当要表示种类时,它可视为可数名词,即a fruit 指一种水果,fruits 指多种水果。
比较:fruits Some fruits have thick skins. 有些水果皮很厚。
The potato is a vegetable, not a fruit. 土豆是一种蔬菜,而不是一种水果。
考点名称:一般现在时,动词单数第三人称
一般现在时:
表示现在经常反复发生的动作、存在的状态或习惯性的动作的时态。可概括为
①经常性或习惯性动作;
②长期存在的特征或状态;
③普遍真理、客观事实等。
构成:
一般现在时用行为动词的原形,但第三人称单数作主语时,动词的词尾要加-S。
a. 表示经常性或习惯性的动作。
例:Li Ming always helps the old man. 李明一直帮助这位老人。
We usually go to school on foot. 我们通常步行上学。
They sometimes go fishing on Sundays. 他们有时周日去钓鱼。
b. 表示永恒不变的事实或真理。
例:A bird flies with wings. 鸟用翅膀飞翔。
c. 用在格言、谚语中。
例:Pride goes before a fall. 骄者必败。- 一般现在时具体用法:
1.表示经常的或习惯性的动作,常与表示频率的时间状语连用。
时间状语:
always,usually,every morning/night/evening/day/week/year,often,sometimes,
occasionally,from time to time,twice a week,rarely,seldom,once a month,hardly,ever,never.
e.g: I leave home for school at 7:00 every morning.
2.表示主语具备的性格、能力、特征和状态。
e.g:I don't want so much.
Ann Wang writes good English but does not speak well.
比较:Now I put the sugar in the cup.
I am doing my homework now.
3.表示客观事实和普遍真理。
e.g :The earth moves around the sun.
Shanghai lives in the east of China.
4.在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中,常用一般现在时代替将来时。
5.表示预先计划或安排好的行为。
6.小说故事用一般现在时代替一般过去时。新闻报道类的内容,为了体现其“新鲜”性,也用一般现在时来表示过去发生的事情。
7.有些表示状态和感觉的动词表示现在发生的具体行为时,只用一般现在时,而不用进行时态。
8.表示现在发生的具体动作或存在的状态
9表示格言或警句中。 e.g Pride goes before a fall. 骄者必败。
注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。
例:Columbus proved that the earth is round..
第一句用一般现在时,用于操作演示或指导说明的示范性动作,表示言行的瞬间动作。
再如:Now watch me,I switch on the current and stand back.
第二句中的now是进行时的标志,表示正在进行的动作的客观状况,所以后句用一般现在时。 - 一般现在时用法表:

第三人称单数的构成见下表:
不规则变化have和be动词 变have为has 变be为am,is,are例: have-has; be-am,is,are词
构成
举例
一般情况
词尾+s
动词原形
第三人称单数
work(工作)
stop(停止)works
stops以-ch, -sh, s, x, o结尾
词尾+es
teach(教)
wash(洗)
dress(装扮)
fix(安装)
go(去)teaches
washes
dresses
fixes
goes以“辅音字母+y”结尾
变y为i,再加es
fly(飞翔)
try(尝试)flies
tries 一般现在时的特殊用法:
一些动词可用一般现在时来表达现在进行时:
verbs of the senses: hear,see,taste,smell,feel
verbs of the thinking: believe,know,mean,realize,think,remember
verbs of the linking: dislike,fear,heat,like,love,want
verbs of the possession: belong,have,own,possess
考点名称:现在进行时,现在分词
现在进行时:
表示动作发生的时间是“现在”,动作目前的状态是“正在进行中”。所谓“正在进行中”,是指在谈到这件事的时候,这个动作还在进行中。
现在进行时由“系动词am/ is/ are+动词-ing形式”构成。
例:We are reading the text. 我们正在读课文。
My sister is working in a hospital. 我的妹妹在医院工作。
They are watching TV now. 他们正在看电视。
What are you doing, Li Lei? 你现在正在干什么,李雷?- 现在进行时的基本用法:
A表示现在( 指说话人说话时) 正在发生的事情。
例:We are waiting for you.
B. 表示现阶段正在进行的动作,说话时未必正在进行。
例:Mr. Green is writing another novel.
(说话时并未在写,只处于写作的状态。)
例:She is learning piano under Mr. Smith.
C.已经确定或安排好的但不确定会不会发生的将来活动。
I'm leaving for a trek in Nepal next week.(我下周要去尼泊尔旅行)
We're flying to Paris tomorrow.(我们明天乘飞机去巴黎) 一般现在时与现在进行时的区别:
一、准确理解两种时态的主要含义:
(一)一般现在时:
1.表示事物的本质特性或客观存在,没有时限性。
The table ____ soft。(feels) 表特性特征。
Japan ___ in the east of China。 (lives) 表客观事实
2.现阶段经常性、习惯性的行为,可带频率时间。
The shop closes at 7:30 p.m.
Father doesn’t smoke. (习惯)
3.表说话时的状态,感觉或结果,一般用状态动词,如:It doesn’t matter. Does it hurt? (感觉结果)
4.特殊用法:
-在条件、时间、让步从句中用现在时代替将来。
-If you go there,I’ll help you.
—用在begin,come,go,leave,return,open,close 等短暂谓语动词表规定计划。
The plane takes off at 11:30. (不受主观支配的计划)
-在剧本、解说、标题或there(here)开头的句中表进行
- 最新内容
- 相关内容
- 网友推荐
- 图文推荐
| [家长教育] 孩子为什么会和父母感情疏离? (2019-07-14) |
| [教师分享] 给远方姐姐的一封信 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 伸缩门 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 回家乡 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 是风味也是人间 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 一句格言的启示 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 无规矩不成方圆 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 第十届全国教育名家论坛有感(二) (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 贪玩的小狗 (2018-11-07) |
| [教师分享] 未命名文章 (2018-11-07) |

![Where is my bag? It's _____________the desk. [ ]A. inB. behindC. on-五年级英语](http://www.00-edu.com/d/file/ks/4/1/44/2019-08-20/small3591750882d019139d20d416cb80f64f1566236486.jpg)
![Where's my pen? [ ]A. It's in the desk.B. It's under the desk.C. It's on the desk.-四年级英语](http://www.00-edu.com/d/file/ks/4/1/44/2019-08-20/small4157828d9d6bc1a02bdbdd4d3ffccde61566236790.jpg)
![I can call you _____________ the phone.[ ]A. inB. atC. onD. of-六年级英语](http://www.00-edu.com/d/file/ks/4/1/44/2019-08-20/small17adfe158040ebb20380cac1c81e7ec81566232881.jpg)
